New this year (2015) is The Case for Loving: The Fight for Interracial Marriage by Selina Alko. Illustrations are by Alko and her husband, Sean Qualls.
The author's note tells us that Alko is a "white Jewish woman from Canada" and that Qualls is an "African-American man from New Jersey."
The story of Mildred Jeter and Richard Loving resonated with Alko and Qualls. Their case went before the United States Supreme Court in 1967. Here's the synopsis posted at Scholastic's website:
For most children these days it would come as a great shock to know that before 1967, they could not marry a person of a race different from their own. That was the year that the Supreme Court issued its decision in Loving v. Virginia.
This is the story of one brave family: Mildred Loving, Richard Perry Loving, and their three children. It is the story of how Mildred and Richard fell in love, and got married in Washington, D.C. But when they moved back to their hometown in Virginia, they were arrested (in dramatic fashion) for violating that state's laws against interracial marriage. The Lovings refused to allow their children to get the message that their parents' love was wrong and so they fought the unfair law, taking their case all the way to the Supreme Court — and won!The Loving case is of interest to me, too. We all ought to embrace its outcome. As the synopsis indicates, the story is about the love Jeter and Loving had for each other, and how, using the court system, laws against their desire to be married were struck down. We need to know that history. It is important. In her review in the New York Times, Katheryn Russell-Brown noted its strengths. She also said something I agree with:
Alko’s calm, fluid writing complements the simplicity of the Lovings’ wish — to be allowed to marry. Some of the wording, though, strikes a sour note. “Richard Loving was a good, caring man; he didn’t see differences,” she writes, suggesting, implausibly, that he did not notice Mildred’s race. After Mildred is identified as part black, part Cherokee, we are told that her race was less evident than her small size — that town folks mostly saw “how thin she was.” This language of colorblindness is at odds with a story about race. In fact, this story presents a wonderful chance to address the fact that noticing race is normal. It is treating people better or worse on the basis of that observation that is a problem.
As Russell-Brown noted, the "language of colorblindedness" doesn't work. As a grad student in the 90s, I read research that found that the colorblind approach sent the opposite message to young children.
The Case for Loving also provides us with an opportunity to look at identity and claims to Native identity.
When I first learned that Alko and Qualls presented Mildred Jeter as part Cherokee (as shown in the image to the right), I started doing some research on her and the case. In some places I saw her described as Cherokee. In a few others, I saw her described as Cherokee and Rappahannock. That made me more intrigued! In the midst of that research, I also re-read Cynthia Leitich Smith's Rain Is Not My Indian Name and really appreciate--and recommend it--for lots of reasons, including how Smith wrote about Black Indians.
I continued my research on Jeter and found a particularly comprehensive source: That the Blood Stay Pure: African Americans, Native Americans, and the Predicament of Race and Identity in Virginia by Arica L. Coleman. It was published in 2013. Coleman's book has a chapter about Jeter.
Drawing from magazines, newspapers and court documents of that time and more recently, too, Coleman describes the twists and turns that impacted Mildred Jeter's identity. Most crucial to her chapter is information Jeter gave to her.
Jeter did not identify herself as Black. In an interview on July 14, 2004, she told Coleman (p. 153):
"I am not Black. I have no Black ancestry. I am Indian-Rappahannock."
In The Case of Loving, we read about Mr. and Mrs. Loving going to Washington DC to get married, returning home to Virginia with their marriage license, and, being awoken late one night by the police who asked Richard what he was doing in bed with Jeter.
He pointed to their marriage certificate hanging on the wall.
The marriage certificate--an image of which is in Coleman's book--shows us columns for the male and female applying for the license. Here's the information in the female column:
Name: Mildred Delores Jeter
Color: Indian
She identified as Indian. In Central Point (that's the town they lived in), Coleman writes, there was a (page 161-162):
"racial hierarchy that granted social privileges to Whites, an honorary White privilege to Indians (i.e. access to White hospitals and the White only section of rail and street cars), and no social privilege to Blacks."Isn't that fascinating? There's more. In 1870,
The Jeter surname is also listed in the Rappahannock Tribe’s corporate charter (1974) as a tribal affiliate. Many claim, however, that the Jeters are descended from the Cherokee who allegedly began to intermarry with the Rappahannock during the late eighteenth century. According to one anonymous informant, “The situation regarding Indian identity in Caroline County is very complex. There was a time when many in the Rappahannock community believed that they were Cherokee because that was all they knew.” Neither Mildred nor her brother, Lewis Jeter, supported the claim that their father was Cherokee.A 1997 article in the Free Lance-Star reports that she said she was Indian, with Portuguese and Black ancestry. In 2004 Coleman asked her about the Black ancestry, prefacing her question with a reference to the Rappahannock's historic association with Blacks, Jeter told Coleman that the Rappahannock's never had anything to do with Blacks.
That denial of Black ancestry is striking, particularly since the Supreme Court case was based on her being Black. If I understand Coleman's research, Jeter thought of herself as Indian when she married Loving. When their case went before the Supreme Court, she was regarded as Black. In the last years of her life, she said she was Indian. What was going on?
Her ACLU lawyers, Bernard Cohen and Philip Hirschkop, and Virginia's Assistant Attorney General, Robert McIlwaine--needed her to be Black. Her Indian identity had the potential to derail the arguments they were putting forth.
See, there was an act in Virginia called the "Racial Integrity Act" that was intended to preserve the purity of the White race. In early drafts of that act, white meant a person having only Caucasian blood. But that definition was replaced by the "Pocahontas Exception." The Racial Integrity Act was passed in 1924.
When I read "Pocahontas Exception" --- well, I think it fair to say that my eyebrows shot up and that I leaned towards the screen (reading an e-copy of the book)! What is THAT?!
The Pocahontas Exception allowed Whites to claim to be white, as long as they had no more than 1/16 of the blood of an American Indian.
Chief Justice Earl Warren was presiding over the Loving case. Presumably, he knew about her Indian identity and therefore asked about the Pocahontas Exception. I hope I am correct in my reading of Coleman's research when I say that Warren let it go when he heard McIlwaine's reply to his questions. The law, McIlwaine argued, did not apply to this case because Virginia had two populations of significance to its legislature: a bit over 79% were white and a bit over 20% were colored; therefore, the number of Native people (at less than 1%) was insignificant. Moreover (p. 170):
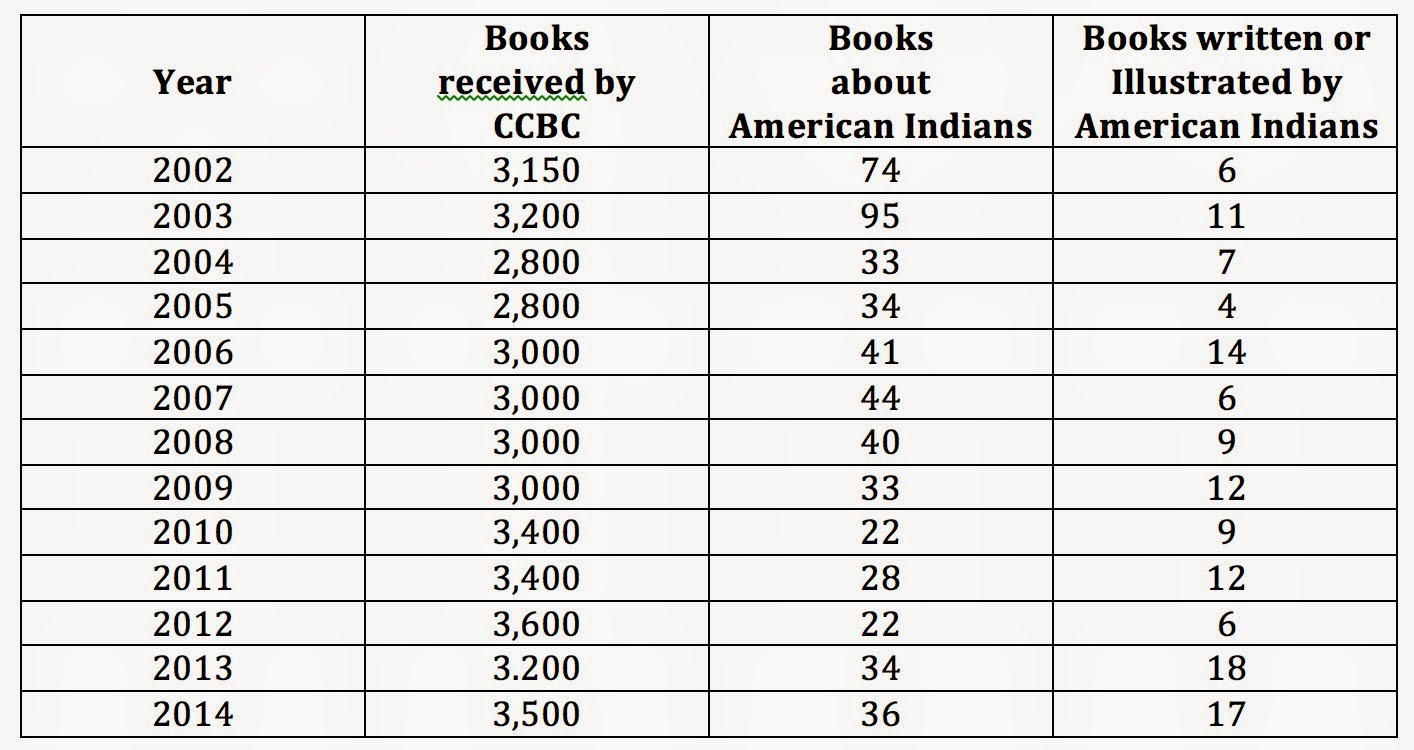
It is a matter of record, agreed to by all counsel during the course of this litigation and in the brief that one of the appellants here is a white person within the definition of the Virginia law, the other appellant is a colored person within the definition of Virginia law.Significant/insignificant are my word choices. McIlwaine didn't use them and neither did Coleman. They are words that resonate with Native people because research studies on race typically have an asterisk rather than data for us, because relative to other demographics, we are deemed too small to count. Indeed, a group of Native scholars have written a book about some of this, titled Beyond the Asterisk: Understanding Native Students in Higher Education.
With intricate detail, Coleman documents how the news media was hit-or-miss in terms of what reporters said about Jeter's race. One day it was "negro" and the next--in the same paper--it was "half negro, half Indian" and then later on, it was back to "negro." In the final analysis, Coleman writes, writers generally describe her as an "ordinary Black woman" (p. 173).
In The Case for Loving, Alko uses "part African-American, part Cherokee" but I suspect Jeter's family would object to what Alko said. As the 2004 interview indicates, Mildred Jeter Loving considered herself to be Rappahannock. Her family identifies as Rappahannock and denies any Black heritage. This, Coleman writes, may be due to politics within the Rappahannock tribe. A1995 amendment to its articles of incorporation states that stated (p. 166):
“Applicants possessing any Negro blood will not be admitted to membership. Any member marrying into the Negro race will automatically be admonished from membership in the Tribe.”I'm not impugning Jeter or her family. It seems to me Mildred Jeter Loving was caught in some of the ugliest racial politics in the country. As I read Coleman's chapter and turn to the rest of her book, I am unsettled by that racial politics. In the final pages of the chapter, Coleman writes (p. 175):
Of course, Mildred had a right to self-identify as she wished and to have that right respected by others. Nevertheless, viewed within the historical context of Virginia in general and Central Point in particular, ironically, “the couple that rocked courts” may have inadvertently had more in common with their opponents than they realized. Mildred’s Indian identity as inscribed on her marriage certificate and her marriage to Richard, a White man, appears to have been more of an endorsement of the tenets of racial purity rather than a validation of White/ Black intermarriage as many have supposed.
Turning back to The Case for Loving, I pick it up and read it again, mentally replacing Cherokee with Rappahannock and holding all this racial politics in my head. It makes a difference.
At this moment, I don't know what it means for this picture book. One could argue that it provides children with an important story about history, but I can also imagine children looking back on it as they grow up and thinking that they were misinformed--not deliberately--but by those twists and turns in racial politics in the United States of America.
Published in 2015 by Arthur A. Levine, I do not recommend The Case for Loving.
~~~~~
Updates to add relevant items shared by others:
Kara Stewart pointed me to a news story from a Virginia TV station:
Doctor's quest to engineer a 'master race' in the early 1900s still hurting Virginia Indian tribes
Kara's comment prompted me to search for information on the Racial Integrity Act. I found that the Library of Virginia has a page about it.
Update, March 18, 7:25 PM:
Just saying again---you must get a copy of Coleman's book. In other chapters, she talks about the Pocahontas Exception and how it was written to accommodate "the White elite who said they were descendants of the Indian princess Pocahontas and the English colonist John Rolfe." Here's one excerpt (p. 5):
It shall hereafter be unlawful for any white person in this State to marry any save a white person, or a person with no other admixture of blood than white and American Indian. For the purpose of this act, the term “white person” shall apply only to the person who has no trace whatsoever of any blood other than Caucasian; but persons who have one-sixteenth or less of the blood of the American Indian and have no other non-Caucasic blood shall be deemed to be white persons.
*Update, March 23, 12:05 PM:
Professor Coleman read my review and noted an error in what I said. I've used the cross-out option to indicate what is wrong and inserted the correct information. Mulatto/Negro were specific to the Jeter name, not to Mildred's Jeter's parents.