Eds. note: A couple of people wrote directly to tell me they're having trouble submitting a comment. If you've had trouble, too, please write to me directly and I'll post on your behalf. If you wish to be anonymous, I will respect your request. My apologies!
I spent the first three days of this week at Georgia State University. I gave a lecture in their Distinguished Speaker series and several guest lectures to classes in GSU's Department of Early Childhood and Elementary Education. All meals were with students and faculty. It was a full schedule, but I enjoyed and learned from all of it and am sharing one part of it here.
Just before I got on my plane for Atlanta on Monday morning (August 31, 2015), I learned (via Facebook) that the author, Deborah Wiles, wished she'd known I was going to be there, because she wanted to meet me. I didn't know her work at that point.
Deborah was able to get an invitation to dinner on Tuesday evening. There were five of us (three professors, Deborah, and myself). I've had meals with writers before, but don't recall one like that one. I was, in short, rather stunned by most of it.
Deborah's experience of it is different from mine. Early Wednesday, she provided a
recap on her Facebook page (note: sometimes that page is viewable, sometimes it isn't; no idea why!):
Last night's dinner at Niramish in Little Five Points, ATL. I got excited when I saw that Debbie Reese was speaking to students in the School of Education at Georgia State and I... um... invited myself to dinner. No I didn't. But I did squee a liitle (a lot) about the fact that she was coming. I was invited to dinner and was ecstatic about the invite, so much so that I brought everyone a book and foisted it into their hands. They were so gracious. I loved talking about children's literature and who gets to tell the story about careful, close reading, and about thoughtful critical discourse (for starters). I have long admired Debbie's work and have been getting to know my teaching friends at the College of Education & Human Development, Georgia State University this year, whom I admire more with each encounter... Thank you the invitation and generosity! Rhina Williams, Cathy Amanti, Debbie Reese, and Thomas Crisp.
I replied to her on Friday afternoon (September 4):
Deborah, you read my blog and my work, so you know I'm pretty forthcoming. I'll be that way here, too. When you brought up the who-can-write topic at dinner, there was an edge in your words as you spoke, at length, about it and criticisms of REVOLUTION. Since then, I've spent hours thinking about that dinner. I don't think we had a discussion, but I am willing to have that discussion with you. You indicate that white writers feel they can't get their books published if their books are about someone outside the writers identity. With regard to non-Native writers writing books about Native people, I don't see what you're describing. What do you think... do you want to talk more about this? On my blog, perhaps?
And she responded:
Sure, we can talk more about that. I want to make sure I am clear about what I said (or tried to say). I don't think white writers can't get their books published if they write outside their culture, not at all... these books are published all the time. I've published them. We were bouncing around quite a bit at that dinner, topic to topic. Part of what I said was that I got push-back in certain circles for writing in Ray's (black) voice in REVOLUTION, but I know that voice is authentic to 1960s Mississippi because I lived there and heard it all my life and wrote it that way. Sometimes in our (collective) zeal to "get it right" we point at a problem that isn't there. I'm happy to talk more on your blog! Thanks for thinking about it with me.
So, here's my post about that dinner. Obviously I wasn't taking notes. Deborah's comment above ("what I said (or tried to say)") demonstrates that neither of us is sure of what was said. This is my recollection and reflections on the evening.
On arriving, Deborah immediately began by talking to me about my work, saying that writers read what I say. She specifically mentioned my work on Ann Rinaldi's
My Heart is on the Ground and how that made an impact on writers.
I was, of course, glad to hear that, but then she turned the conversation to current discussions in children's literature, saying that this is a dangerous time for writers, because they are being told that they can't write outside their cultural group and that if they do write outside their culture, their books won't get published. Note that in her Facebook comment above, she said these books are getting published and uses her book as an example. I recall saying that I think these are exciting times, because we need diverse voices. It was that exchange--with her characterizing these times as dangerous and me describing them as exciting--that set the tone for the rest of the evening.
Deborah started talking about her book,
Revolution. She said that she'd shown Jackie Woodson some of the work she was doing on that book, or that she'd talked with her about the African American character, Ray, in
Revolution, or maybe it was that she'd talked with Jackie about white writers giving voice to black characters. Whatever it was, the outcome was that Deborah had a green light (my words, not hers) from Jackie. I don't doubt any of it, but I am uneasy with that sort of report. It implies an endorsement from someone who isn't there to confirm it. I'm very attentive to this because, knowingly or not, writers who do that are, in my view, appropriating that person in a way that I find inappropriate. If Deborah could point to a statement Jackie made about
Revolution, that would be different.
Deborah went on to to tell us that she had lived in Mississippi and that the voice she gave to Ray
is based on what she heard when she lived there. But, she said, "fervent" people didn't like what she did. Someone (me or one of the professors at the table) asked her who the "fervent" people are, and she said that she wasn't going to say if I was going to tell them.
I was taken aback by that and responded immediately with "well don't say then, because I will tell them." She went on to say that it is SLJ's Heavy Medal blog, and that Heavy Medal discussions are dangerous, that they have too much power in terms of influencing what people think.
Deborah seemed angry. She was talking at me, not with me. I don't recall saying anything at all in response to what she said about Heavy Medal and fervent people.
I share my recollection of the dinner--not to solicit sympathy from anyone or to embarrass Deborah--but to convey my frustration with the incredible resistance Deborah's words and emotion represent within the larger context of children's literature.
The who-can-write conversation is not new. In 1996, Kathryn Lasky wrote an article titled "To Stingo with Love: An Author's Perspective on Writing outside One's Culture." In it, she wrote that "self-styled militias of cultural diversity are beginning to deliver dictates and guidelines about the creation and publishing of literature for a multicultural population of readers" (p. 85 in Fox and Short's
Stories Matter: The Complexity of Cultural Authenticity in Children's Literature, published in 2003 by the National Council of Teachers of English).
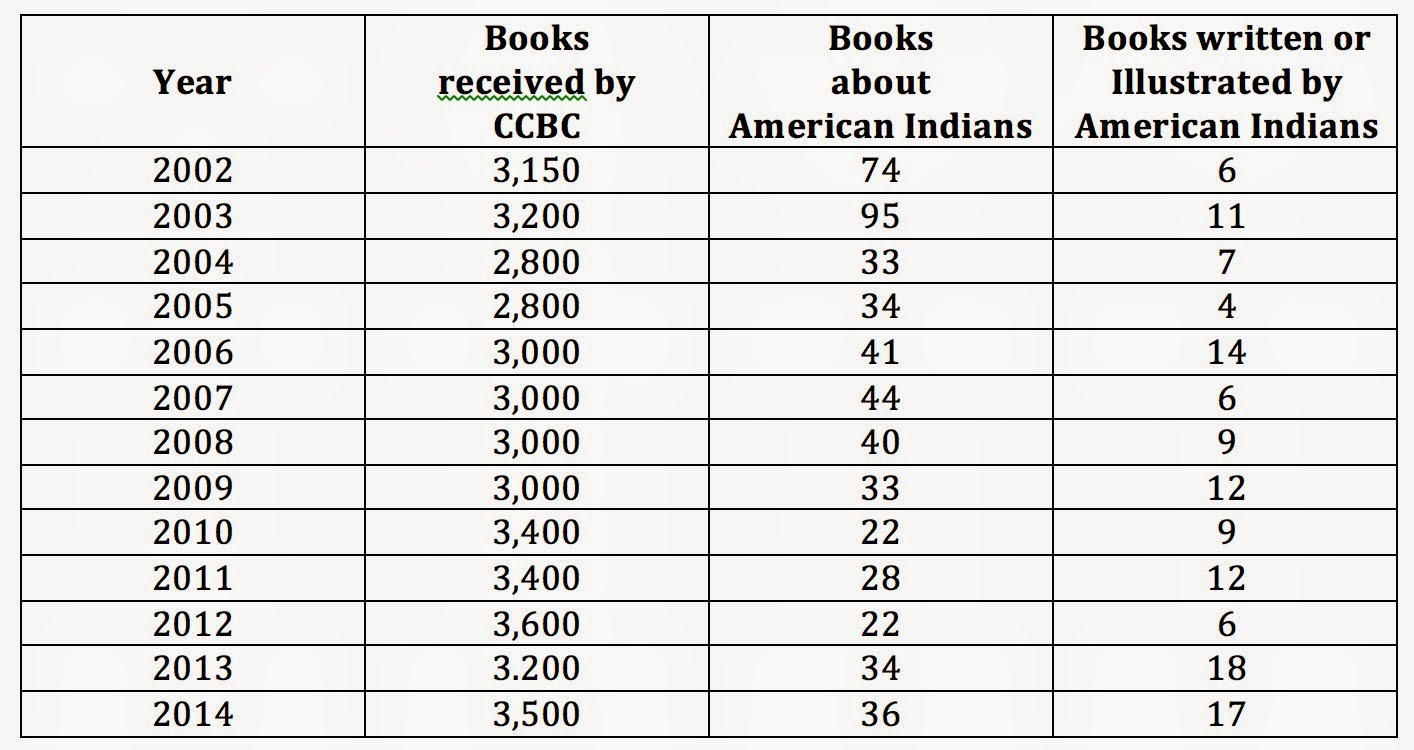
I count myself in that "self styled militia." One need only
look at the numbers the Cooperative Children's Book Center at the University of Wisconsin puts out each year to see that we've made little progress:

CCBCs data shows some small gains here and there, but overall, things haven't changed much. One reason, I think, is the lack of diversity within the major publishing houses. I think there's a savior mentality in the big publishing houses and a tendency to view other as less-than. For some it is conscious; for others it is unconscious. All of it can--and should be--characterized as well-intentioned, but it is also unexamined and as such, reflects institutional racism. The history of this country is one that bestows privilege on some and not on others. That history privileges dominant voices over minority ones, from the people at the table in those publishing houses to the voices in the books they publish. That--I believe--is why there's been no progress. Part of what contributes to that lack of progress is that too many people feel sympathy for white writers rather than stepping away from the facts on who gets published.
At the end of the meal, Deborah brought out copies of her books to give to us. I got the picture book,
Freedom Summer but it felt odd accepting the gift, given the tensions of the evening. I think she was not aware of that tension. She ended the evening by praising my blog but the delivery of that praise had a distinct edge. She banged the table with her fist as she voiced that praise.
I hope that my being at that dinner with Deborah that evening and in the photograph she posted on Facebook aren't construed by anyone as an endorsement of her work. Yesterday, I went to the library to get a copy of
Revolution, because, Deborah said she is working on a book that will be set in Sacramento, and, she said, it will include the Native occupation of Alcatraz. I want to see what her writing is like so that I can be an informed reader when her third book comes out.
Before going to the library, I looked online to see if there was a trailer for it. In doing that, I found a
video of Deborah reading aloud at the National Book Award Finalists Reading event. Watching it, I was, again, stunned. She read aloud from chapter two. Before her reading, she told the audience what happened in chapter one. The white character, Sunny, is swimming in a public pool, at night. She touches something soft and warm, which turns out to be a black boy. She screams, he runs away. Then she and Gillette (another white character) take off too, but by then, the deputy is there. She tells him what happened. The last lines of that chapter are these (page 52):
There was a colored boy in our pool. A colored boy. And I touched him, my skin on his skin. I touched a colored boy. And then he ran away, like he was on fire.
As readers of AICL know, I keep children foremost in my mind when I analyze a book. In this case, how will a black child read and respond to those lines? And, what will Deborah think of my focus--right now--on that part of her book? I haven't read the whole book. No doubt, people who read AICL will be influenced by my pointing out that part of the book. Will Deborah think I am, like the people at Heavy Medal, "dangerous"?
Deborah said, above, that "
Sometimes in our (collective) zeal to "get it right" we point at a problem that isn't there." She means the people who criticized her for Ray's voice in
Revolution. The dinner and Deborah's remarks are the latest in a string of events in which people in positions of power object to "fervent" people.
Jane Resh Thomas did it in a lecture at Hamline and
Kate Gale did it in an article at Huffington Post.
I'll wind down by saying (again), that I've spent hours thinking about that dinner. It seemed--seems--important that I write about it for AICL. This essay is the outcome of those hours of thinking. I was uncomfortable then, and I'm uncomfortable now. I wanted to say more, then, but chose to be gracious, instead. I'm disappointed in my reluctance then, and now. I don't know where it emanates from. Why did I choose not to make a white writer uncomfortable? Is Deborah uncomfortable now, as she reads this? Are you (reader) uncomfortable? If so, why? Was Deborah worried about my comfort, then, or now? Does it matter?!
I can get lost in those questions, but must remember this: I do the work I do, not for a writer, but for the youth who will read the work of any given writer. For the ways it will help--or harm--a reader's self esteem or knowledge base.
The imagined audience for
Revolution isn't an African American boy or girl. It is primarily a white reader, and, while the othering of "the colored boy" in chapter two may get dealt with later in the book, all readers have to wait. Recall the words of
Anonymous, submitted to AICL as a comment about Martina Boone's
Compulsion. They have broad application:
I find the idea of a reader -- particularly a child -- having to wait to see herself humanized an inherently problematic one. Yes, it might accurately reflect the inner journey many white people take, but isn't the point that our dehumanizing views were always wrong? And therefore, why go back and re-live them? Such ruminations could definitely be appropriate in an all-white anti-racist group, in which the point is for white people to educate each other, but any child can pick up a book, and be hurt--or validated--by what's inside. Asking marginalized readers to "wait" to be validated is an example of white dominance as perpetuated by well-intentioned white folks.
It is long past time for the industry to move past concerns over what--if anything--dominant voices lose when publishers actually choose to publish and promote minority voices over dominant ones. It is long past time to move past that old debate of who-can-write. Moving past that debate means I want to see publishers actually doing what Lasky feared so that more books by minority writers are actually published.
In 1986, Walter Dean Myers
wrote that he thought we (people of color) would "revolutionize" the publishing industry. We need a revolution, today, more than ever. Some, obviously, won't join this revolution. Some will see it as discriminatory against dominant voices but I choose to see it as responsive to children and the millions of mirrors that they need so that we reach a reality where the publishing houses and the books they publish look more like society. In this revolution, where will you be?
To close, I'll do two things. First is a heartfelt thank you to Dr. Thomas Crisp at Georgia State University, for years of conversation about the state of children's literature, and, for assistance in writing and thinking through this essay. He was at that dinner in Atlanta. Second is a question for Deborah. Why did you want to meet me? Usually, when people want to meet me, there's a quality to the meeting that was missing from our dinner in Atlanta. There's usually a meaningful discussion of something I've said, or, about the issues in children's literature. That didn't happen in Atlanta. In the end, I am left wondering why you wanted to meet me.
Update, September 6, 2015
Several readers submitted comments. Please read them. They are quite thoughtful. Deborah Wiles submitted a comment, too. I am inserting it here, in the body of the original post, for your convenience.
Debbie Wiles said...
Hi, Debbie, I just want to say that I enjoyed meeting you on Tuesday evening, and was looking forward to it all day. I don't believe these are dangerous times to be publishing for young people, I don't believe writers are being censored by publishers in what they write (that's not my experience), and I do believe writers are getting published when they write outside their cultures. I did say that wielding power for personal gain can be dangerous, and that thoughtful, critical, informed discourse is important. My experience of the conversation was different from yours. We bounced around all over the place with different topics, weaving in and out. Everyone laughed a lot. I had a good time. I was glad to be included. I agreed with you that these are exciting times to be publishing! They are. I still think you should write the book about the Occupation of Alcatraz. My best, Debbie Wiles
A similar conversation regarding this topic took place on Twitter yesterday. B. R. Sanders responded to it. Please read
A Response to Colten Hibbs and Maggie Stiefvater on Writing the Other
And--if you're having trouble submitting a comment, you can send it directly to me and I'll post it on your behalf.
Update, September 6, 2015 - evening
Maggie Stiefvater wrote
a response to the pushback she got on her post on writing the other. I highly recommend it.











.jpg)


